mPEG-SIL
$100.00 – $360.00
mPEG-Silane (mPEG-SIL) is available in molecular weights of 2,000, 5,000, 10k and 20k.
Packaged in 1 gram and 5 gram bottles.
Shipping charges will be calculated based on the total order.
Description
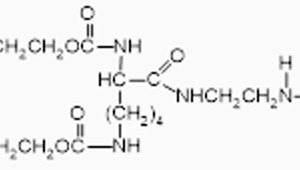
mPEG silane, is a linear polyethylene glycol chain with a silane group at one end of a PEG chain and a methoxy group at the other end. PEG is a hydrophilic polymer known for its water solubility and biocompatibility, Silane PEG is a surface reactive product used to modify and deactivate glass, silica, metal, ceramics and hydroxylated surfaces and particles.
Structure and Properties:
- PEG silane consists of a PEG chain attached to a silane group, which is usually a trimethoxysilane or triethoxysilane.
- They exhibit excellent adhesion properties to various substrates.
Uses and Applications:
- Surface modification: PEG silanes are widely used to modify the surface properties of materials, making them more hydrophilic, biocompatible, or resistant to fouling.
- Coatings: They can be used to create coatings with enhanced water repellency, antifouling, and anti-corrosion properties.
- Biomaterials: PEG silanes are employed in the development of biomaterials for medical implants, tissue engineering, and drug delivery.
- Sensors: They are used in the fabrication of sensors for detecting various analytes, including biological molecules and chemicals.
- Chromatography: PEG silanes are used as stationary phases in chromatography to separate and analyze compounds.
Reaction Conditions:
- pH: The pH of the reaction medium can significantly influence the reactivity of PEG silanes. The optimal pH range for hydrolysis and condensation reactions is typically between 2 and 7.
- Temperature: The reaction temperature can affect the rate of hydrolysis and condensation. Higher temperatures generally accelerate the reaction.
- Solvent: PEGs are readily soluble in dichloromethane, chloroform, acetonitrile and water at room temperature.
- PEGs require heat to be soluble in toluene, methanol, ethanol, and isopropanol.
- PEGs are not soluble in ethers, ethylene glycol, hexane, and are not soluble in most alcohols at room temperature.
- Catalyst: Catalysts, such as acidic or basic catalysts, can be used to accelerate the hydrolysis and condensation reactions.
Additional information
| Molecular Weight | 10K, 2000, 20K, 5000 |
|---|---|
| Bottle Size | 1 gram, 5 gram |