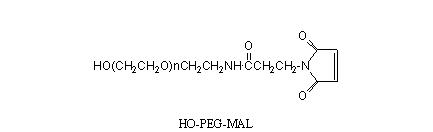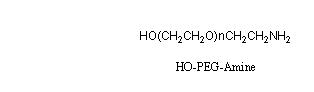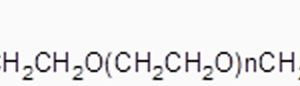HO-PEG-NH2
Price range: $200.00 through $695.00
HO-PEG-Amine (HO-PEG-NH2) is available in molecular weights of 2,000, 3,400 and 5,000.
This product will be bottled in 1 gram or 5 gram bottles, depending on the item you order.
Other MW available as custom products contact our Sales Team.
Shipping charges will be calculated based on the total order.
Description
HO-PEG-NH2 (Hydroxyl PEG Amine) is a heterobifunctional polyethylene glycol (PEG). This product has two different reactive functional groups at each end of the PEG chain, a hydroxyl (-OH) group and an amine (-NH2) group. This structure is a versatile tool in the biomedical research and drug development fields.
- Bioconjugation and Crosslinking: This is one of its most significant applications. The hydroxyl and amine groups can be selectively reacted with other molecules, allowing for the attachment of various biomolecules (like proteins, peptides, antibodies, nucleic acids, or small molecules) to surfaces or to each other.
- The amine group is highly reactive with NHS esters, carboxylic acids (in the presence of activating agents like EDC or HATU), and carbonyls (aldehydes/ketones) to form stable amide or imine bonds.
- The hydroxyl group can also be activated for conjugation, for example, by converting it to an active ester, allowing for further modifications.
- This dual functionality allows for the creation of complex molecular constructs or for tethering molecules in a specific orientation.
- Drug Delivery Systems (PEGylation): PEGylation is the process of covalently attaching PEG to a therapeutic molecule or nanoparticle. HO-PEG-NH2 is frequently used for this purpose due to the benefits of PEGylation:
- Increased Solubility: PEG is hydrophilic, so conjugating it to hydrophobic drugs can significantly improve aqueous solubility.
- Prolonged Circulation Time: PEG forms a protective hydration shell around the attached molecule, reducing its recognition and uptake by the reticuloendothelial system (RES), thereby increasing its half-life in the bloodstream.
- Reduced Immunogenicity: PEG can mask the immunogenic sites of proteins or peptides, reducing the risk of an immune response.
- Targeted Delivery: The reactive ends of HO-PEG-NH2 can be used to attach targeting ligands (e.g., antibodies, peptides, or small molecules) to drug carriers (like nanoparticles or micelles), enabling them to selectively accumulate at diseased sites (e.g., tumors).
- Formation of Polymeric Micelles/Nanoparticles: HO-PEG-NH2 can be used to synthesize block copolymers (e.g., PEG-PLGA) that self-assemble into micelles or nanoparticles capable of encapsulating and delivering drugs.
- Surface Modification: The presence of reactive functional groups allows HO-PEG-NH2 to be used for modifying surfaces of various materials (e.g., biosensors, medical implants, or diagnostic platforms). This can:
- Reduce Non-Specific Binding: PEG layers create a “stealth” effect, preventing non-specific adsorption of proteins and other biomolecules, which is crucial for reducing biofouling and improving assay sensitivity.
- Immobilize Biomolecules: The reactive groups can be used to covalently attach specific biomolecules to surfaces, creating functionalized interfaces for diagnostic or therapeutic applications.
- PEG Hydrogels and Biomaterials: HO-PEG-NH2 can serve as a building block for creating PEG-based hydrogels or other polymeric materials. The functional groups can be crosslinked to form a network, which can be used in tissue engineering, drug encapsulation, or as a scaffold for cell growth.
Additional information
| Molecular Weight | 2000, 3400, 5000 |
|---|---|
| Bottle Size | 1 gram, 5 gram |